Understanding Body Structure and Nutrition
Scientific foundations of how nutrition, movement, and lifestyle support human body composition and tissue health. This is educational content designed to explain fundamental concepts.

Body Composition Fundamentals
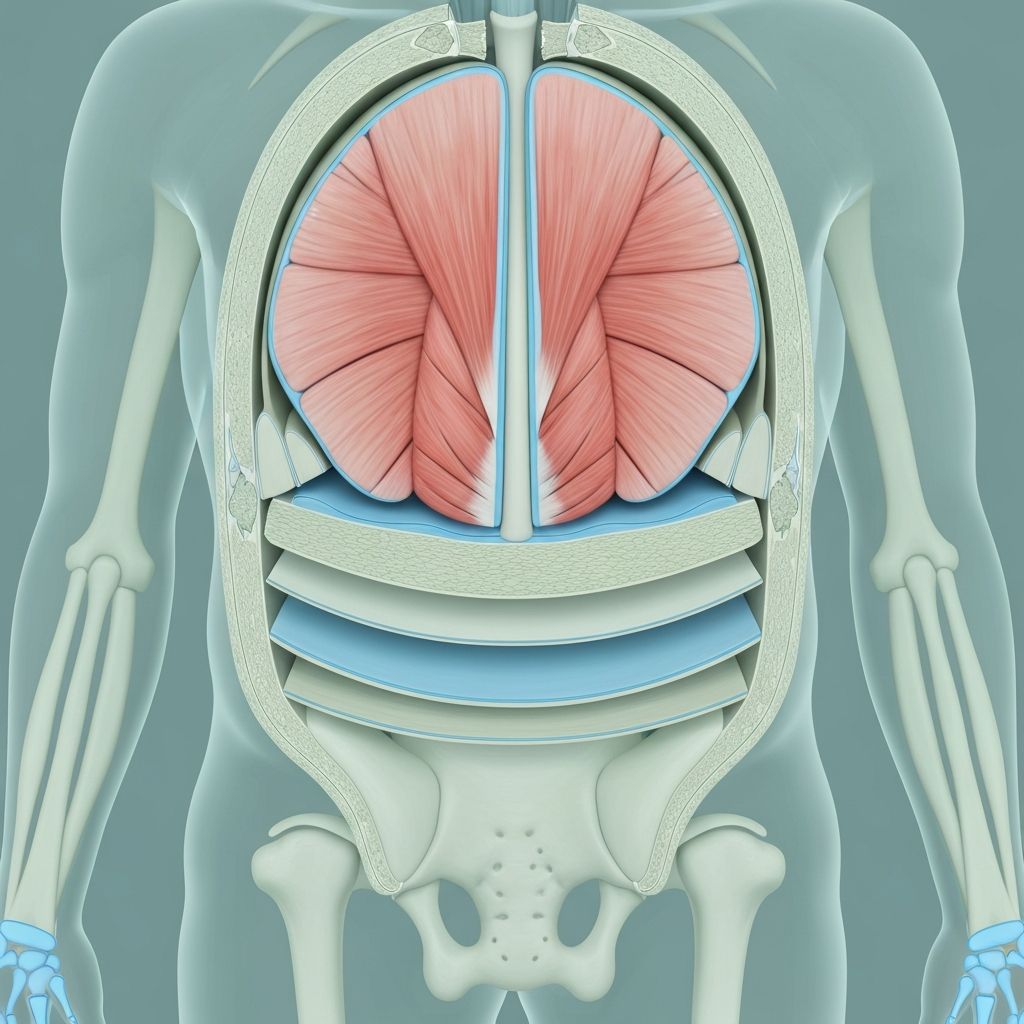
Body composition refers to the relative proportions of different tissue types in the human body. The primary components include skeletal muscle, bone, adipose tissue (fat), and water. Understanding these fundamental structures helps explain how nutrition and movement influence overall health and physical function.
Skeletal muscle tissue is metabolically active and responds to physical activity and adequate protein intake. Bone structure provides support and undergoes constant remodeling influenced by mechanical stress and mineral availability. Adipose tissue serves essential functions including energy storage and hormone production. Water comprises a significant portion of body weight and is critical for cellular function.
Common Questions About Body Structure
Nutrition and Tissue Building

Macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—each play distinct roles in body structure and function. Proteins provide amino acids essential for muscle tissue maintenance and synthesis, enzyme production, and immune function. Carbohydrates supply energy for cellular function and physical activity. Fats support hormone production, vitamin absorption, and cellular structure.
Micronutrients including vitamins and minerals are essential cofactors in metabolism and tissue maintenance. Calcium and phosphorus support bone structure; iron supports oxygen transport; zinc supports immune function and tissue repair. A varied diet of whole foods ensures adequate intake of these essential nutrients for tissue health.
Movement and Structural Support
Regular movement is fundamental to maintaining healthy body structure. Physical activity stimulates muscle tissue adaptation, increases bone density, supports cardiovascular health, and enhances metabolic function. Different types of movement provide different benefits: weight-bearing activities support bone health, resistance-based movement supports muscle maintenance, and cardiovascular activity supports heart and metabolic health.
Sedentary behavior is associated with muscle atrophy, reduced bone density, and metabolic decline. In contrast, consistent daily movement, even at moderate intensity, supports tissue maintenance and overall structural health. The combination of varied movement types—walking, strength work, and flexibility—provides comprehensive structural support.
Explore More Science
Body Composition Science Explained
Detailed exploration of the scientific principles underlying body composition and tissue structure.
Read the full explanation →
Nutrition's Role in Body Tissues
How macronutrients and micronutrients support tissue development and maintenance.
Learn more science →
Movement and Structural Health Basics
Research insights on how physical activity maintains and develops body structures.
Discover the facts →Continue Exploring
TheBodyBlueprint provides neutral, evidence-based information about body structure and nutrition science. All content is educational in nature and does not constitute professional advice.
Explore All Articles